Apple shook the privacy advocates in its recent developer note, and people are baffled with the latest announcement. Apple decided to eliminate the “Do Not Track” feature from the upcoming version of Apple Safari browser.

Why Apple is Removing “Do Not Track”?
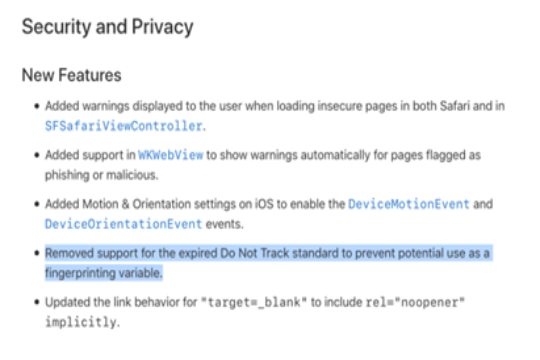
The ‘Do Not Track’ feature is meant to prevent the use of a fingerprint variable.
Apple in the developer note said that the feature (do not track) is being misused on PC and mobile browsers, and removing it will help make browser experience better for the users. The change is expected to be carried out in the next major mobile and PC operating system update.
Privacy advocates are worried that this may hinder the future of privacy and if other browsers follow Apple footprints, then the situation will get more worst.
Alan Toner a special adviser at Electronic Frontier Foundation, a digital rights organization, said:
“[Do Not Track] lures users into some sense of false security. Users think that it is protecting, but it is not”
Additionally, Toner said:
“It is important (Do Not Track) because it allows people to express their privacy preferences to companies; however, there are no regulations that abide companies to go with what people desire.”
Privacy advocates think that removing this feature from Safari will undermine any belief in the utility of the system while others hope that after this move Apple will introduce new ways to protect consumers.
Apple’s move is the latest blow to the years-long hard work by internet companies. Many browsers have the Do Not Track feature added which gave people the power to turn it on or off when needed voluntarily.

Other Browsers
Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox have the feature on their browser and have not confirmed or announced if they have the plan to remove it or not.
Apple is the first company to remove Do Not Track feature, and as per the company there is no ideal replacement for it right now, but there are some security measures that can stop certain companies to track user’s online activity.
As per Apple, Safari has intelligent tracking prevention which limits companies to use third-party cookies and track users. Mozilla Firefox, on the other hand, has a more or less similar feature which is called “Enhanced Tracking Protection” which blocks third-party cookies and does not allow trackers to store any information.
Intelligent Tracking Prevention is designed to block cookies and cross-site tracking.
How to Turn on Prevent Cross-Site Tracking?
To be sure that you have that settings turned on go to Settings > Safari > Privacy and Security > Turn on Prevent Cross-site tracking.
If you are using iOS 12.2 or MacOS 10.14.4, then you will notice that the setting for Do Not Track me is gone. Advocates argue that without universal standard legislation there is no other way to ensure privacy measures unless companies start respecting internet users and don’t log off their data.
When a user switches on Do Not Track feature, then a voluntary signal is sent to the website saying that this user does not wish to be tracked.
The website, however, is not bound to follow that signal, and it is upon their wish if they want they can. So if you have Do Not Track enabled, then there is nothing that is preventing the website from tracking you away.
Apple’s decision is said to be in response with the fact that Do Not Track project quietly ended in January 2019. Moreover, this privacy option was also redundant as the company announced built-in-anti-tracker in 2017 which aims to block cookies.
Intelligent Tracking Prevention 2.0
The new Intelligent Tracking Prevention 2.0 is already enabled as per the latest update. It can be found under Safari’s privacy setting.
The Intelligence Tracking Prevention feature is already included in iOS 12 update and macOS Mojave. According to Apple, this feature is much useful to stop cookies. Additionally, it helps prevent cross-site tracking without explicit consent.
Other than that, Apple has also taken a few measures to ensure that the latest Safari browser equips up with improved personal control and online privacy.
- Safari will now warn users of the websites that do not have an SSL certificate.
- Safari will also warn sites that are flagged as malicious or as phishing sites.
- Further, Safari will log people automatically to sites when ‘Auto Save Passwords’ will fill in credentials on a website.
The commitment from Apple to ensure privacy is applaudable and is good for users that do not want their business-related online activities tracked without any express permissions made.
This is also good for the future of digital security as online identities are used as weaponry to exploit a major attack like fraud and to bypass infrastructure security.
Why does it matter?
Tracking on the web is now becoming a trend as advertisers are looking forward to peeking in the personal details on users. Do Not Track was an admirable effort but it lacked regulation behind it.
Apple’s new method of intelligence tracking is a perfect way to restrict those prying advertisers, it would be great to see Google coming on board by adding this feature in Chrome.
Some argue that Apple’s decision of axing Do Not Track feature in Safari will not affect privacy. The alternate “Intelligent Tracking Prevention” is enough to ensure the user’s privacy online.
This new alternate was launched in 2017 and it uses machine learning to identify ad track behavior. Moreover, it prevents adversaries from following the user’s movement as they jump from one URL to another.
Author Bio: Marko Phillips